
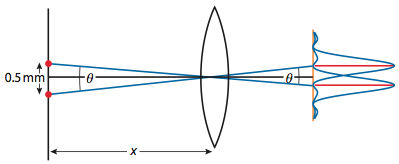
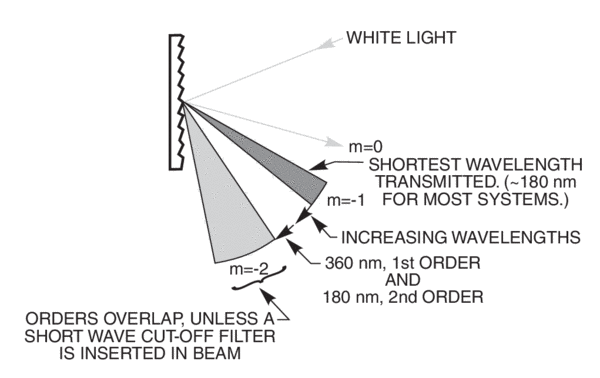
The diffraction of a given narrow beam of light (corresponding to a single wavelength) with the help of a grating will produce a bright beam straight ahead and a series of beams to either side at angles where the light waves from adjacent slits reinforce each other. What is the cause of diffraction? Explanation: Diffraction occurs due to interference of secondary wavelets between different portions of a wavefront allowed to pass across a small aperture or obstacle. The diffracted X-rays generate a pattern that reveals structural orientation of each atom in a given compound. The phenomena by which X-rays are reflected from the atoms in a crystalline solid is called diffraction. What is X-ray Diffraction and what are its application in chemistry? A1. The phenomenon is the result of interference (i.e., when waves are superimposed, they may reinforce or cancel each other out) and is most pronounced when the wavelength of the radiation is comparable to the linear dimensions of the obstacle. What is diffraction waves?ĭiffraction, the spreading of waves around obstacles. The amount of diffraction depends on the wavelength of light, with shorter wavelengths being diffracted at a greater angle than longer ones (in effect, blue and violet light are diffracted at a higher angle than is red light). In a monochromator it is only the first order diffraction (either +1 or -1) that is used to select the desired wavelength and the higher orders are unwanted. These patterns of interference rely on the size of the diffracting object and the size of the wave.ĭiffraction at higher orders follows a similar pattern of increasing angle away from the normal and reducing intensity. Interference can be either constructive or destructive. This shift will cause the wave to have interference with itself. … What causes diffraction to occur?ĭiffraction is caused by one wave of light being shifted by a diffracting object. Since light waves are small (400 to 700nm), diffraction only occurs through small openings or small grooves, with the greatest diffraction occurring when the size of the opening is the same order of magnitude as the wavelength of light. The bending and spreading of light as it interacts with obstacles. What is required in order for a diffraction to occur? 11 What is an example of a diffraction pattern?.10 What is the formula for diffraction grating?.5 What is the cause of diffraction Mcq?.1 What is required in order for a diffraction to occur?.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
